Robotic Automation Solutions

We Provide Best RPA
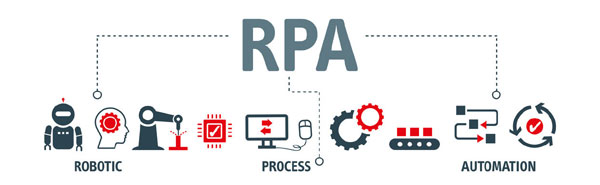
What is Robotic process automation (RPA)??
RPA is the use of software with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to handle high-volume, repeatable tasks that previously required humans to perform. These tasks can include queries, calculation and maintenance of records and transactions Because RPA doesn’t replace employees, it can be attractive to many types of organizations. For example, because RPA typically doesn’t require changes to legacy systems or applications, the changeover from traditional processing processes is much easier than with other automation solutions. RPA is also a great option for industries that need human interaction and are highly regulated.
RPA technology consists of software robots(bots) that can mimic a human worker. RPA bots can log into apps, enter data, calculate, and complete tasks and then log out. Currently practitioners divide RPA into two camps—screen scraping and object recognition. Screen scraping is the most common type of RPA used today. It involves the bots mimicking a human’s mouse movements to capture data, which is then fed into an application or back-end system. Object recognition uses live video, or a static image to train a bot to recognize individual objects and their features. It is the most complex of RPA technologies currently available, but it has the highest level of accuracy. Some example tasks include AI-based robotic process automation technology that can be used for data entry, managing documents, writing emails.
RPA technology into three broad categories: probots, knowbots and chatbots.
- Probots are bots that follow simple, repeatable rules to process data.
- Knowbots are bots that search the internet to gather and store user-specified information.
- Chatbots are virtual agents who can respond to customer queries in real time.

Robotic process automation streamlines workflows, which makes organizations more profitable, flexible, and responsive. It also increases employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity by removing mundane tasks from their workdays.
The typical benefits of robotic automation include reduced cost; increased speed, accuracy, and consistency; improved quality and scalability of production. Automation can also provide extra security, especially for sensitive data and financial services.
Robotic automation is a best-fit solution for organizations that have become highly dependent on manual processes. It can also increase the redeployment of human resources and reduce the risk of fraud, waste, or error.
**According to research from Gartner, RPA in healthcare improves efficiency by automating data collection and records retrieval
 The hosting of RPA services also aligns with the metaphor of a software robot, with each robotic instance having its own virtual workstation, much like a human worker. The robot uses keyboard and mouse controls to take actions and execute automations. Normally all these actions take place in a virtual environment and not on screen; the robot does not need Process automation is the process of using software to control computers without the need for human interaction. This method can be scaled thanks to virtualization technology that enables a company with limited physical hardware capacity and heavy costs. RPA implementations in corporations have shown dramatic cost savings when compared to non-RPA approaches. There are however several risks with RPA. Criticism includes risks of stifling innovation and creating a more complex maintenance environment of existing software that now needs to consider the use of graphical user interfaces in a way they weren’t intended to be used. RPA also carries the risk of moving all PC functions into the cloud, which has been damaging to many, these risks are important considerations for businesses looking to implement RPA. There will be a net benefit from the trend of robotic process automation in developed countries with skills and technological infrastructure to develop and support this technology.
The hosting of RPA services also aligns with the metaphor of a software robot, with each robotic instance having its own virtual workstation, much like a human worker. The robot uses keyboard and mouse controls to take actions and execute automations. Normally all these actions take place in a virtual environment and not on screen; the robot does not need Process automation is the process of using software to control computers without the need for human interaction. This method can be scaled thanks to virtualization technology that enables a company with limited physical hardware capacity and heavy costs. RPA implementations in corporations have shown dramatic cost savings when compared to non-RPA approaches. There are however several risks with RPA. Criticism includes risks of stifling innovation and creating a more complex maintenance environment of existing software that now needs to consider the use of graphical user interfaces in a way they weren’t intended to be used. RPA also carries the risk of moving all PC functions into the cloud, which has been damaging to many, these risks are important considerations for businesses looking to implement RPA. There will be a net benefit from the trend of robotic process automation in developed countries with skills and technological infrastructure to develop and support this technology.
RPA actual use:
- Banking and Finance Process Automation
- Mortgage and Lending Process
- Customer Care Automation
- E-Commerce Merchandising Operation
- OCR Application
- Data Extraction Process
- Fixed automation process
**Meanwhile, Professor Willcocks of the London School of Economics and Political Science speaks of increased job satisfaction and intellectual stimulation, characterizing the technology as having “the ability to take [humans] out of the robot”.
**An article in Computer Weekly suggests that, while projects implemented with traditional process automation tools have helped speed up business processes.
 Our Blue Prism Tutorial provides the basic and advanced concepts of Blue Prism. This tutorial is designed for helping both beginners and professionals.
Our Blue Prism Tutorial provides the basic and advanced concepts of Blue Prism. This tutorial is designed for helping both beginners and professionals.
This tutorial gives you an introduction to Blue Prism along with a wide range of topics such as why use Blue Prism, the history of Blue Prism, Blue Prism architecture, features of Blue Prism, and components of Blue Prism, benefits of using Blue Prism, installation, etc
Blue Prism is a UK based software development company in the field of automation. The company has come up with one of the leading RPA tools, also named Blue Prism. The Blue Prism tool is mainly used to develop software robots that help in automating mundane tasks and eliminating manual work. The term RPA, which is an acronym of ‘Robotic Process Automation’, was first introduced by the Blue Prism group.
Blue Prism helps business operations to be agile and cost-effective by automating repetitive, rule-based, manual back-office tasks. Instead of a manual workforce, Blue Prism makes use of ‘Digital Workforce’, which results in improved accuracy, better security, more compliance, and resilience. The tool is based on Java Programming Language and provides easy to use interface with a visual designer. It allows us to use flow-chart like interface with basic drag and drop functionalities for automating business processes step by step.
History of Blue Prism
 Blue Prism was initially introduced in 2001 by a group of some process automation professionals. The primary aim of Blue Prism was to introduce a technology that could provide the digital workforce and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes. First, Blue Prism focused on back-office processes as there was an enormous unfulfilled requirement for process automation. The company was co-founded by David Moss and Alastair Bathgate, and they delivered a technology that can perform manual work just like a human. This approach was called RPA or Robotic Process Automation.
Blue Prism was initially introduced in 2001 by a group of some process automation professionals. The primary aim of Blue Prism was to introduce a technology that could provide the digital workforce and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes. First, Blue Prism focused on back-office processes as there was an enormous unfulfilled requirement for process automation. The company was co-founded by David Moss and Alastair Bathgate, and they delivered a technology that can perform manual work just like a human. This approach was called RPA or Robotic Process Automation.
Back in 2003, Blue Prism came up with its first commercial product called ‘Automate’. The company kept working on it and increasing the quality of the product. In 2005, the company launched the second version of Automate with more advanced features released explicitly for large scale processing. It helped Blue Prism to achieve the positive impact and trust of customers. Therefore, most of the co-operative financial services started using Blue Prism for automating their business tasks in customer services.
Due to continuous improvement and following a top-down approach, Blue Prism helped enterprises automate their business process in an agile and cost-effective manner and reduce the overall human workforce and timelines.
Why Blue Prism
 With its powerful digital workforce and self-learning visual designer interface, Blue Prism continuously helps users automate billions of processes. The tool has gained an edge over its competitors as it includes better flexibility, security, scalability, compliance, and resilience. Apart from that, Blue Prism has some of the unique features that end customers are getting. These features are helping users to increase productivity, and save hundreds of millions of work hours.
With its powerful digital workforce and self-learning visual designer interface, Blue Prism continuously helps users automate billions of processes. The tool has gained an edge over its competitors as it includes better flexibility, security, scalability, compliance, and resilience. Apart from that, Blue Prism has some of the unique features that end customers are getting. These features are helping users to increase productivity, and save hundreds of millions of work hours.
Blue Prism is the only RPA tool which:
- does not require IT skills to implement.
- does not require any coding skills or programming knowledge.
- can be implemented in a short duration of time (typically 4 to 8 weeks depending on the complexity of the automation process).
- is low cost and affordable compared to the other RPA tools in the market.
- can be implemented within IT infrastructure and processes without making changes to the existing environment.
- creates software robots and supports the digital workforce of enterprise-scale and industrial length.
- provides tremendous ROI that has been as high as 80% and even more.
- offers excellent payback with self-funding returns.
Components of Blue Prism
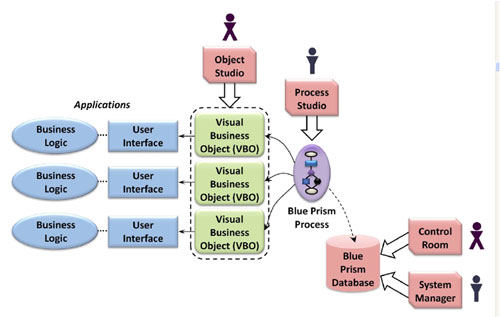
There are a total of four main components present in Blue Prism, such as:
- Process Diagram
- Process Studio
- Object Studio
- Application Modeller
Process Diagram
The Process Diagram is defined as the workflow of business processes, that acts as a program. Because Blue Prism is a Java-based RPA tool, these diagrams can make use of core concepts and basics of programming and create the entire operational workflow like flow-chart. These flow charts are nothing but graphical representations of workflows that help analyze, create, modify, or scale the overall business capabilities.
The processes in workflows enable us to implement automation in the same way humans would operate them manually. But, these processes are based on the digital workforce and use the logic of software robots. The software robots act in the same way humans would be interacting with the applications and system activities to follow sequences of steps to carry out the required results.
Process Studio
The area in Blue Prism that allows us to create Process Diagrams is known as the Process Studio. All the processes are displayed similar to a flowchart. It is one of the main components of Blue Prism as it contains core features such as variables, business logic, control loops, object calls, etc. These all can be used inside any business flow sequentially and tested flawlessly. The created process flow can be considered as a depiction of a human.
Apart from that, a process flow can also contain a sequence of steps required to interact with other system applications to achieve the required results. Each process flow that we create using Process Studio contains the Main Page, which is executed first.
Object Studio
One of the basic requirements for enterprises is to interact and communicate with external applications to automate their business processes efficiently. It is impossible to use Process Studio for this need; therefore, Blue Prism provides another component called Object Studio. Object Studio is the module that enables us to create Visual Business Objects, usually referred to as VBO. These objects are nothing but diagrammatical programs that help in interacting with external business applications.
In this component, one business object is responsible for offering an interface that can interact with only one external application. Unlike Process Studio, each object in Object Studio does not contain Main Page. Besides, it contains two default pages that are organized as a flat group.
Application Modeller
Application Modeller is the embedded capability within the Object Studio. It is generally used to create application models with Object Studio. It consists of configuration required to interact with the existing applications and UI elements. These elements are identified by software bots based on specified attributes. The elements are further configured and updated to make them unique for every single element. The software bots can then interact with these elements and perform specified operations over them.
Blue Prism Architecture
The architecture of RPA Blue Prism can be classified into the following four elements:
- Process Studio
- Object Studio
- Control Room
- Release Manager
Process Studio
When it comes to the Blue Prism architecture, Process Studio is the most useful element. It enables businesses to create the best process for automation. It helps design, build, test, and modify the automation processes within the Blue Prism tool. These processes are designed in such a way that they can be reused from the concerned objects.
In Blue Prism, most of the processes are very similar, and they follow the same structure for automation. We can call and process objects at any time as per the project’s requirements. The primary function of Process Studio is to provide sequential processes that are dynamic, reusable, and flexible. To achieve this functionality, the processes are configured with business logic, and results are obtained in the least possible time. Process Studio has several components that allow us to automate complex business processes efficiently.
- The libraries of business objects are contrasted as per the project’s requirements
- The actions and activities are implemented using drag and drop features in a sequential and well-defined structural workflow representation.
- The actions are inserted with the combination of control loops, business logic, and object calls. These actions are further controlled in the hierarchy situated in the Process Layer.
- The actions and activities are defined in sequence and tested in a flow that remains visible to users all the time.
Object Studio
Object Studio is another essential element in the Blue Prism architecture. It is mainly used when we require objects in Blue Prism that can be used multiple times. These reusable objects are typically considered as the building blocks for the automation of complex business processes. This approach helps to use existing objects and implement them with current applications as well as external applications.
Apart from that, there are several default objects available in Blue Prism that can be directly used to automate various tasks. They can also be modified when required. These default objects are designed to accomplish the automation of basic system tasks.
- Almost all the applications can be easily modeled and further explored to build an array of multiple screens with the help of system elements of Object Studio.
- Developers can encapsulate all the required interactions directly to the nodes. It is one of the most critical actions followed using Object Studio in the Blue Prism automation approach.
- Few other commonly used actions include making changes to the fields, full-scale validation of data, and description of the data, etc.
- The best thing is that the user can control these actions and recall them multiple times.
Control Room
The control room in Blue Prism architecture is defined as the command center. That means it can be used to control, monitor, schedule, and execute automation processes to the digital workforce.
In other words, all the resources in the Blue Prism architecture are monitored and controlled through Control Room. The control room is nothing but a centralized administration console inside the Blue Prism tool that displays insights of the entire process workflow. It allows us to check the startup and the entire working of a process through a manual approach, which means we can select specific information for detailed statistics to ensure proper working.
- Process scheduling in Control Room makes the execution of certain processes (which are lengthy) easier as these processes can be scheduled for auto-execution when systems are ideal.
- The control room displays real-time stats and insights of what the software robots are currently doing, at what speed and how effective they are.
- It also provides run logs that precisely define what actions have been performed by software robots. It will also cover such actions and activities that could not be executed due to any reason.
Release Manager
Release Manager in Blue Prism architecture is mainly responsible for performing activities whose primary purpose is to release automation processes. It also helps in automating and streamlining the functions related to the management. In simple words, it is used to manage, import, verify, and export configuration packages across various Blue Prism environments. Also, the release manager provides options to create, delete, and modify packages. It contains details of previously created and imported releases of packages.
- It consists of a tool that can be used to manage the import and export of configuration packages (such as created processes and instructions) between different environments.
- It offers visibility of packages that were created somewhere else and then imported in Blue Prism.
- It provides the ability to manage updates for current as well as newly created processes across the environment.
Blue Prism Features
The main features of RPA Blue Prism are explained below:
Robust: Blue Prism offers many robust features such as data encryption, load balancing, and end-to-end auditing, etc. Because of end-to-end audit support, every change in the automation process is audited, and results are provided to the related user.
Accurate: Blue Prism allows us to automate any number of business processes. There is no limit of tasks that we can automate and execute using this RPA tool. It delivers expected results with the same accuracy for any number of processes each time.
Secure: Blue Prism provides a secure environment for the user. It offers safe and secure control over its virtual and digital workforce, which also includes software robots.
Scalable and Resilient: With its central management control feature, Blue Prism offers a scalable and resilient environment. It makes the process automation easier. Every process can be automated as per the business requirements and can be monitored centrally.
Consistent: The tool is designed to work consistently without human intervention. Because Blue Prism uses the digital workforce (use of software robots), it can work 24*7 without taking any gap, and every activity happening on the system can be easily tracked.
Analytics: Blue Prism has advanced features that help in configuring analytics of the entire session and software robots. The statistics or the session information can be transferred to the monitoring systems and can be easily seen on Dashboards.
Data Abstraction with Security: Blue Prism can work and operate autonomously. All the operations are performed and stored within the data center. It results in increased process-security and well-defined data abstraction.
Cloud Support: Blue Prism also provides cloud-support that extends its functionalities to complete automation tasks as per the business requirements. This also makes it easier to manage and control software robots centrally. Users are only required to create digital workers for process automation.
Smart Execution: With its smart execution feature, Blue Prism robots can easily connect to systems. They further react dynamically to the responses in the data on different environments.
Availability of Multiple Formats: Blue Prism allows automation of several file formats, such as CSV, Excel, PDF, XML, and all types of image files.
Multi-platform Support: Blue Prism is designed to automate software written in Java, Mainframe, or other windows applications. It can also automate the code that is developed for web-based applications.
Benefits of Using Blue Prism
Few of the main benefits of Blue Prism are listed below:
- No need for IT skills for the implementation.
- Easy-implementation support. Blue Prism can be easily implemented in 4 to 6 weeks, depending on the complexity of the processes.
- Automation support for application management and fields, irrespective of their on-screen position and behavior, results in increased bot performance.
- Improved interactivity and productivity of bots because of custom digital front-office and back-office agents.
- Efficient and effective end-to-end automation.
- Offers a robust and rich feature-based analytics suite.
- Availability of double-byte character set to automate processes that require double-byte. For example- Asian languages.
- Use of multi-tiered encryption algorithms that includes more secure access, connectivity, data storage, and many other functionalities.
- Supports secure process automation with its custom permissions feature. It allows user-specific access and authorization to robots, robot groups, and processes.
- Provides Enterprise-specific password vaults system with certified CyberArk Credential Management and Control to include consistent enterprise-specific credentials.
- Real-time feedback from the improved Control Room Module. It also provides detailed information and real-time insights of software robots.
- Provides excellent payback with self-funding returns and the highest possible ROI.
Difference between Popular RPA Tools
There are several RPA tools present in the market. However, UiPath and the Automation Anywhere are the other most popular RPA tools along with the Blue Prism. The main differences between these RPA tools are tabulated below:
| Attributes | Blue Prism | UiPath | Automation Anywhere |
| Popularity | More Popular than Automation Anywhere. | Most Popular RPA tool. | Least Popular when compared with Blue Prism and UiPath. However, it is popular enough than other RPA tools. |
| Usability | User-friendly visual designer providing automation on the go. UI is simpler than Automation Anywhere. | Extremely User-friendly with easy to use visual designer. | Because of complexity, it is best suitable for developers. |
| Product Availability | Comes with the 30 days of the trial period. | Provides a community edition that is lifetime-free and easy to operate. It helps to understand the features available in the full paid version. | Comes with 30 days of the trial period to provide a quick overview of its features and functionalities. |
| Software Bots | Mainly used for back-office automation. | Used for both front-office and back-office automation. | Used for both front-office and back-office automation. |
| Recorders | Recorders are not available in this RPA tool. It supports only drag and drops features for process automation. | Recorders are available, and recorded actions can be modified as per requirements. It has multiple recording options. | Recorders are available, and recorded actions can be modified as per requirements. |
| Cognitive Capability | Low-level cognitive capability. | Medium Level Cognitive Capability. | Medium Level Cognitive Capability. |
| Access | Provides application-based access. | Provides both the application and browser-based access. | Provides application based entrance. |
| Coding Requirements | Supports coding, but it is not mandatory. | Supports recorders and drag and drops; hence, coding is not required. | Supports recorders and drag and drops; hence, coding skill is not mandatory. |
Jobs and Future Scope of Blue Prism
Blue Prism is an RPA tool that interacts with rule-based processes of organizations and provides automation with a digital workforce. Blue Prism is one of the leading and popular RPA tools known for coining the term ‘RPA’. It is known as one of three top companies that are said to be a leader in process automation using the digital workforce. It has gained popularity with its market presence as well as the quality of its products and offerings.
Therefore, the future in Blue Prism has a positive side. Most of the organizations are showing their interest and investing their money, time, and resources. With Blue Prism, companies are achieving a better ROI as compared to the human workforce. The tool is eventually helping companies to streamline their business operations and efficiently automate them. Additionally, Blue Prism is continuously updating its product and adding new features to enhance the quality and performance of products.
As the use of RPA tools is rapidly increasing day by day, there are more opportunities for jobs than before. One can get a job like Blue Prism Developer as a fresher or Blue Prism Manager with 1-2 years of experience. Having 1-2 years of expertise in Blue Prism will benefit an employee with a good amount of salary.
Prerequisite
There is no specific prerequisite for this tutorial. All you need is continuous learning and practicing with the tools. However, if you want to extend functionalities to match your requirements, then a basic knowledge of software coding and programming logic will be beneficial and put you at an advantage.
Audience
Our Blue Prism Tutorial is designed to help beginners and professionals.
Problem
We assure you that you will not find any difficulty while learning through our Blue Prism Tutorial. But if you find any mistake in this tutorial, we request you to kindly post the problem in the contact form so that we can improve it.
Banking and Finance Process Automation
The banking sector in itself is a critical one, mainly because the sector has an enormous number of unstructured data making up for some amount of immaturity. Because of this complexity, RPA has been able to take the maximum advantage of automation in order to reduce workload and enhance productivity.
RPA has been significantly adopted in this sector, for making the time-consuming banking operations more organized and automated. According to reports, the largest revenue share for 2019 was dominated by BFSI segment in terms of application of RPA.
Robotic process automation has been a tremendous help in simplifying labor-intensive tasks for bank employees. By shifting these monotonous, back-office jobs to machines, banks have relieved humans of tedious and repetitive responsibilities, which in turn has led to increases in efficiency levels and staff performance.
RPA can do many things in the Banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) industry. One of these is to free up a person so they can work on more important tasks.
. Customer Service
. Compliance
. Accounts Payable
. Credit Card Processing
. Mortgage Processing
. Fraud detection
. Know Your Customer (KYC)
. General Ledger
. Report Automation
. Account Closure Process
. Account Origination & Receivable
. Surrender
. Collection
. Underwriter Support
. Deposits & many more
RPA has been able to do this by replacing the repetitive tasks with automated solutions and bringing in a more efficient flow of data. RPA system does not just stop at processing routine information, but also using intelligent reasoning to identify patterns and extract relevant information from huge amounts of data that often go unnoticed by human analysts.
Bank employees are confronted with voluminous data from customer and manual processes, which is prone to have errors. Banks around the world are considering RPA to avoid this problem by minimizing the amount of manual processing required in order to correct these errors. Banks also spend a lot of time manually processing large amounts of data, which takes up valuable staff.
Benefits of RPA in Banking & Finance:
. Customer Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are improved
. Operational agility is raised
. Customer trust and loyalty is enhanced
. Revenue and cash flow are increased
. Processing time is reduced
. Customer churn is lowered
. Customer experience is enhanced
. Business response time is reduced
. Regulatory compliance is improved
. Scalability
. Increased operational efficiency
. Cost-effectiveness
. Risk and compliance reporting
. Availability
. Zero infrastructure cost
. Faster implementation
. Business growth with legacy data
RPA’s next big thing in Banking and Finance will be in Customer-Facing Applications. Banks are already using RPA to reduce the time taken for customer enquiries, providing greater transparency into their financial situation, allowing banks to serve customers better. This is only the beginning of where RPA can take us with its endless possibilities.
Mortgage and Lending Process
A mortgage loan or simply mortgage is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or alternatively by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged.
What is RPA for Mortgage and Lending Process?
The financial services industry, such as banking, is the best place for robots. The problem with banks is that there are many repetitive tasks and a lot of documents and compliance directives. Robots can do these things very well.
Lending customers today expect a lot from their lenders, and it’s largely due to all the technology on offer. They want instant responses to inquiries and online portals which can process requests anytime anywhere. If they have questions, many of them will look for an automated Chatbot before considering other options like helpline or walk-in branches.
Loan application, processing and closing management RPA functions can be used to automate the loan origination process. Roles that may benefit from RPA include staff responsible for collecting customer information; compiling loan details, attributes, and risk scores; applying underwriting rules to determine eligibility
RPA Use Cases in the Mortgage & Lending Industry:
- RPA Workflows Make Processes More Consistent, Reliable, Faster, Better Defined, and Control Costs
- Faster Loan Processing & Loan Cycle Time
- Improved Visibility into the Lending Process
- Easy Lending Audit
- Better Customer Experiences in General & Diverting Traffic to New Channels
Robot Process Automation (RPA) can make processes more consistent and better defined. It can help control costs and make the process faster. RPA also makes it easier to do an audit of the lending process, which means people have a better understanding of what happens during that process. In general, it will make customers’ experiences much.
Customer Care Automation
Businesses use customer service automation when they want to solve customer problems but not with people. They can do it using self-service resources or by sending messages anytime someone has a problem.
What is RPA for Customer Care Automation?
Robotic process automation is a customer service system that reduces human involvement in solving customer inquiries. Businesses achieve robotic process automation using self-service resources, proactive messaging, or simulated chat conversations.
RPA Use Cases for Customer Service:
- Chatbots are a way to answer customer service questions. They can also become more transactional with the help of RPA technology.
- Self-service is a way for customers to use the back of the application.
- Using RPA, customers can walk into a store and a robot will be there to help them. They can have their own login information.
- The security can be improved by using robots. Robots avoid mistakes that humans would make. This improves the quality of work and makes people obey the rules better.
Benefits of integrating RPA for customer services
- Reduced costs
- Simplified desktops
- Improved processes
- Better experiences
- Easy deployment
E-Commerce Merchandising Operation
As technology advances, the e-commerce marketplace is experiencing a major transformation from an industry that was once largely unorganized to one that has become much more efficient and customer centric.
Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Augmented Reality are already widely used in e-commerce and have brought benefits to both retailers and customers. A technology that contributes to the development of e-commerce is robotic process automation or RPA.
By deploying robotic process automation, e-commerce retailers will be able to manage their business more efficiently and with higher levels of organization.
What is RPA for E-commerce?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is a service that allows e-commerce companies to hire cloud-based software robots for as little as 2 hours per week. This means you can get all the benefits of robotic process automation without having to invest in your own licensing and software. It’s a good solution for small businesses and larger ones.
RPA is a cross-platform, cross-discipline technology that automates manual tasks within an organization’s computer systems. Originally designed and deployed for IT support and disaster recovery organizations, the application of RPA is now rapidly evolving into diverse sectors including finances, healthcare automation.
Different applications of RPA in an e-commerce:
- You can make the most of your time and update your inventory every week.
- Creating online shopping content is hard. There are many things to think about, such as how the text will be laid out and how people will click on different things.
- Products are organized into categories.
- RPA is being used in the new field of supply chain management.
- One of the important functions of a returns processing department is to check on any returned items.
- RPA is a way to improve customer service. With it, companies can provide better service by doing jobs that are repetitive or time-consuming for humans.
OCR Application
OCR is the process of converting text in images to machine-encoded text. This can be done with a scanned document, a photo of a document, or from subtitle text superimposed on an image.
What is RPA for Optical Character Recognition (OCR)?
Optical character recognition (OCR) is a necessary component of any good robotic process automation (RPA) solution. Essentially, OCR technology converts typed, handwritten, or printed text into machine-encoded text that can then be used later in electronic business processes without input from the user.
OCR is a good idea for any robotic process automation. OCR is how you get text that you see in images or documents into the computer and then use it as data.
OCR has been around in various forms for more than 100 years, but newer versions of the technology use AI to recognize and capture data with high levels of accuracy.
RPA OCR use cases:
- Most companies want to become digital. They have a problem of storing documents, so they don’t digitize them. But most companies still process invoices in hard formats- there are no digital copies for them.
- Using robots instead of people to do data entry is a good idea. Robots can read both typed and handwritten data. They are also easy to upgrade and will work well in complex processes.
- Advanced OCR can find potentially suspicious data, so we’ll verify it for correctness and afterwards reinsert that data.
- A robot can help you if you scan information from a customer application and put it into a CRM system. The robot will do the text analysis, so that the right category is chosen. If there is an irregularity, then the robot will tell a human to fix it.
- Know Your Customer is important because people can be who they say they are. Robots can read the name on a person’s identification card and then check to see if it matches the name on their application form. If there is a difference, the robot might ask for help from humans. Robots learn from how humans do things in other ways too.
Benefits of RPA in OCR:
- 1.Unburdening data validation departments. This will help people get their work done faster.
- 2.Documents are going faster.
- 3.Advanced technology is being used in more processes.
Data Extraction Process.
Data extraction is the process of retrieving information out of (usually unstructured or poorly structured) data sources and transforming it into a more easily processed format for later usage.
What is RPA for Data Extraction Process?
Data extraction is among the best ways to speed up operational efficiency, so look into robotic process automation.
Example: The problem with data extraction through RPA is that it doesn’t refine the information. This can result in a host of different errors being created which could be even worse than ones caused by human error.
Businesses can also use robotic process automation for automated web data extraction. This will help them increase speed and efficiency while transforming unstructured content into structured and high-quality information.
Benefits of RPA in Data Extraction
- Robotic process automation (RPA) is a set of technologies that makes it possible to configure software or applications to automate tasks, without the need for customized user interfaces.
- Robotic process automation is a constantly evolving and expanding tool that offers many advantages for both enterprise-level business management as well as small businesses.
- Tracking is a way to see where you are going. It helps you know how fast you are going and what direction you are facing.
The most common challenges with robotic process automation are scaling up and any risk of a global pandemic – or other large-scale disaster.








